Niobrara shale play is rich with gas processing opportunities
J. Stell, Contributing Editor
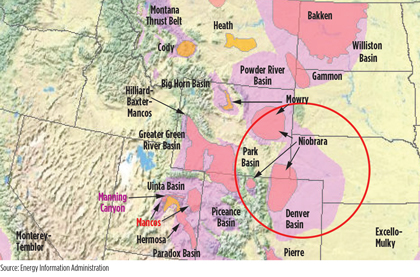
The unconventional Niobrara shale play (Fig. 1) lies in the US Rocky Mountain region. In Colorado, the play is found in the North Park basin in the northeastern portion of the state, the Sand Wash basin in the northwest, and the Denver-Julesburg (DJ) basin in northeastern Colorado and southwestern Nebraska. The play extends into the southern portion of the Powder River basin of southeastern Wyoming and into northwestern Kansas. To date, Weld County is thought to be the center of the Niobrara boom, boasting more than 18,000 gas and oil wells.
 |
|
Fig. 1. The Niobrara shale lies in the North Park basin and the DJ basin in northeastern |
The play’s oil and rich natural gas production brings a wealth of opportunities for gas processing operators and their associated equipment and service suppliers. While many processing facilities already exist in the area, new facility construction and expansions are underway to accommodate the play’s continued activity.
Aka Energy Group LLC, headquartered in Durango, Colorado and owned by the Southern Ute Indian Tribe, operates the Gilcrest gas plant and related gas gathering systems in the DJ basin near Greeley, Colorado, to process Niobrara wet gas (Fig. 2). The facility includes a 20-million-cubic-feet-per-day (MMcfd) cryogenic processing facility and a 1,000-barrel-per-day (bpd) fractionation unit. In addition to gathering gas on Aka’s own gathering systems, gas volumes are delivered to the Gilcrest plant from independent gas gathering systems.
 |
|
Fig. 2. Aka Energy Group processes Niobrara rich gas via its cryogenic processing facility |
Anadarko Petroleum Corp., based in The Woodlands, Texas, formed Western Gas Partners, a midstream subsidiary, and owns the Wattenberg gas gathering and processing system in the DJ basin. The system includes facilities acquired from EnCana Corp. (Third Creek, Ione, Aristocrat and lateral gathering systems), Kerr-McGee Corp. (Wattenberg gathering system and Fort Lupton plant) and BP Plc (Wattenberg plant), and provides nearly 300 MMcfd of cryogenic processing capacity.
Anadarko plans to expand its Wattenberg capacity with the addition of Lancaster train 1, which is expected to be online in the first quarter of 2014, and train 2, which will be completed in the first quarter of 2015. Each new train will be capable of processing 300 MMcfd of gas.
Crestwood Midstream Partners LP and the owner of its general partner, Inergy LP, announced in July 2013 that Crestwood’s subsidiary, Crestwood Niobrara LLC, completed the acquisition of a 50% interest in Jackalope Gas Gathering Services LLC. The other 50% interest in Jackalope is owned by Access Midstream Partners LP.
The Jackalope facility includes a 120-MMcfd gas processing plant in Converse County, Wyoming. It is estimated to produce approximately 16,275 bpd of liquids and is sited in the Powder River basin of the Niobrara shale play.
DCP Midstream LLC, based in Denver, Colorado, began operations at its new O’Connor plant in October 2013. The O’Connor plant, sited southwest of Kersey, Colorado, is a deep-cut cryogenic processing plant serving the DJ basin. The plant has an initial capacity of 110 MMcfd, and an expansion to 160 MMcfd is expected to be completed by the third quarter of this year. The project includes amine and molecular sieve dehydration inlet treating, gas liquids recovery and refrigeration, and gas compression. In total, DCP will increase its gathering and processing assets in the DJ basin to nine gas processing plants with a total capacity of approximately 800 MMcfd and NGL production of 70,000 bpd. Presently, the nine plants include the Eaton, Greeley, LaSalle, Lucerne, Lucerne 2, Mewbourn, Platteville, Roggen and Spindle facilities.
Enterprise Products Partners LP receives Niobrara gas from Summit Midstream Partners LP’s Grand River gathering system, and processes the production at its 1.7-Bcfd Meeker 2 processing facility in Meeker, Colorado. The Piceance basin facility has a processing capacity of 1.5 Bcfd, with the capability to extract as much as 70,000 bpd of NGL.
Noble Energy Inc., based in Houston, Texas, plans to expand its midstream infrastructure in the area to include gas processing expansions of 900 MMcfd by 2015. Also, in a break from the norm, the company plans to construct and operate a $45-MM LNG facility in rural northern Weld County. The LNG plant, which will be the first of its kind in Colorado, will have the capacity to produce up to 100,000 gallons per day of LNG.
Noble plans to use production from the facility to fuel the company’s rigs and fracturing equipment used in its DJ basin operations. Noble Energy also expects to make LNG production available for other oil and natural gas producers and LNG users in the area. Construction of the facility, which will operate in conjunction with the company’s Keota gas processing plant, will begin by the third quarter of 2014.
Meadowlark Midstream Company LLC, owned by Summit Midstream Partners LLC and based in Dallas, Texas, commenced startup of its Niobrara gathering and processing system in the DJ basin in Weld County, Colorado, in September 2013. The system includes 89 miles (mi) of low-pressure gathering pipeline and a 20-MMcfd cryogenic processing plant.
Western Gas Partners LP was formed by Anadarko to own, operate, acquire and develop midstream assets to gather, process, compress, treat and transport gas, condensate, NGL and oil for Anadarko and third-party producers and customers. In the Rocky Mountains, Western Gas operates the Bison, Chipeta, Fort Union, Granger, Hilight, Platte Valley, Red Desert and Wattenberg complexes.
The Bison treating facility in the northeastern corner of Wyoming consists of three amine treaters with a combined capacity of 285 MMcfd. The facility provides CO2 treating services for the coalbed methane gas gathered from the Powder River basin. The asset includes three 5,230-hp compressors, five generators and the Bison Pipeline, which is operated by TransCanada Corp.
The Chipeta complex includes a natural gas processing plant with three processing trains; the Natural Buttes plant; and a 100% partnership-owned, 17-mi NGL pipeline connecting the Chipeta plant to a third-party pipeline. Chipeta is connected to both Anadarko’s Natural Buttes gathering system and to the Three Rivers gathering system owned by Ute Energy and a third party. The system includes the recent addition of a 300-MMcfd cryogenic plant and has a total processing capacity of 970 MMcfd. The plant sends NGL through a 17-mi pipeline to the Mid-America Pipeline, which provides transportation through the Seminole Pipeline in West Texas and, ultimately, to the NGL markets at Mont Belvieu, Texas, and along the Texas Gulf Coast.
The Fort Union system is a 324-mi gathering system operating within the Powder River basin of Wyoming, and consists of three parallel pipelines and a CO2 treating facility at the Medicine Bow plant. The facility is capable of treating and blending more than 1 Bcfd.
Located in Sweetwater County, Wyoming, the Granger system consists of a gas processing facility, an 810-mi gathering system and eight field compression stations with a total of 43,950 hp. The processing facility includes 200 MMcfd of cryogenic processing, 200 MMcfd of refrigeration processing and 9,500 bpd of NGL fractionation capacity.
The Hilight plant includes a refrigeration facility with a capacity of approximately 60 MMcfd and provides for fractionation of the recovered NGL.
The Platte Valley system, sited in the DJ basin, consists of a processing plant with a cryogenic capacity of 100 MMcfd, two fractionation trains, a 1,105-mi gathering system and related equipment. The Platte Valley processing facility, with a capacity of 85 MMcfd, is primarily supplied by the Wattenberg field.
Western Gas Partners’ Red Desert gathering and processing system is in Sweetwater and Carbon counties in Wyoming. The facilities gather, compress, treat, process and fractionate gas and NGL. The system consists of two cryogenic gas processing plants with a total current operating capacity of 173 MMcfd.
The Wattenberg system is in the DJ basin and consists of a 1,870-mi gas gathering system and the Fort Lupton processing plant, which includes two trains with a total combined processing capacity of 105 MMcfd.
Future buildouts. According to IHS Global Inc., approximately $7.5 billion was spent from 2012–2013 to increase gas processing capacities throughout the US. During that period, an estimated 12 Bcfd of gas processing capacity was added or restarted to serve the boom of US unconventional shale plays, such as the Niobrara. The capacity surge represents almost 20% of total US natural gas demand.
The buildout indicates that operators believe that US demand for natural gas and NGL will continue to rise, along with expected sales prices. Established gas processing operators, along with new entrants into the play, will continue to serve Niobrara rich gas production. Most processors are considering future expansions of their existing facilities, as well as new facility construction. GP
 |
Jeannie Stell is an award-winning writer and editor focused on the upstream, midstream and downstream energy industry. Her articles have been published in several languages, and referenced in white papers by Microsoft and Iranian National Oil Co., and her photographs have been featured on industry magazine covers and in feature editorials. Ms. Stell is the founder of Energy Ink and can be reached at jstell@energyink.biz.




Comments